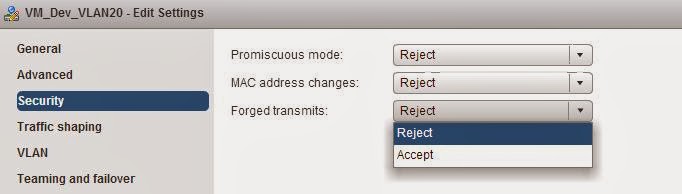
This post explains you the step by step procedure to manually assign network adapters of ESXi host as uplink adapters to your distributed switch. Network adapters can be assigned to distributed switch when adding ESXi host to dvswitch. However this post helps you to understand how manually assign the network adapters as uplinks for distributed switch.
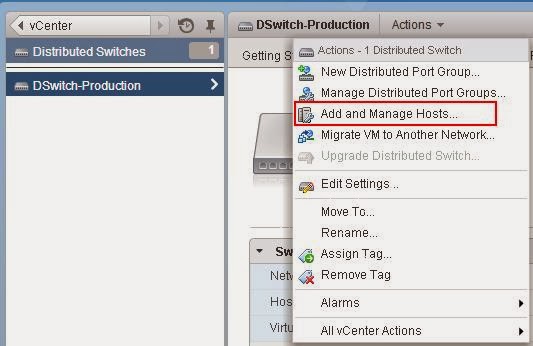
Select your distributed switch from vSphere web client and click on Actions tab, Select Add and Manage Hosts.
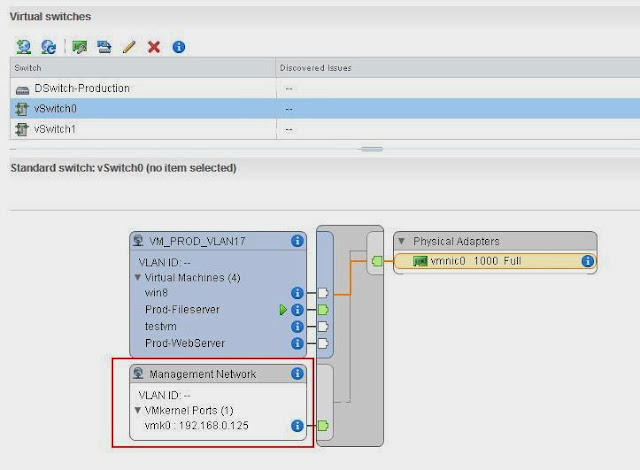
Select your ESX/ESXi host from the list to perform the action. I have selected the host (192.168.0.125) and click on Next
Select Manage Physical adapters checkbox and click on Next.
Select the physical network adapter of the ESXi host to assign and click on Assign Uplink and click on Next. I have selected vmnic3 of ESXi host (192.168.0.125) to assign it to dvswitch
Select the uplink from the below list for vmnic3 adapter and click on Ok.
vmnic3 is assigned state for the Uplink2 for the dvswitch (DSwitch-Production) and click on Next.
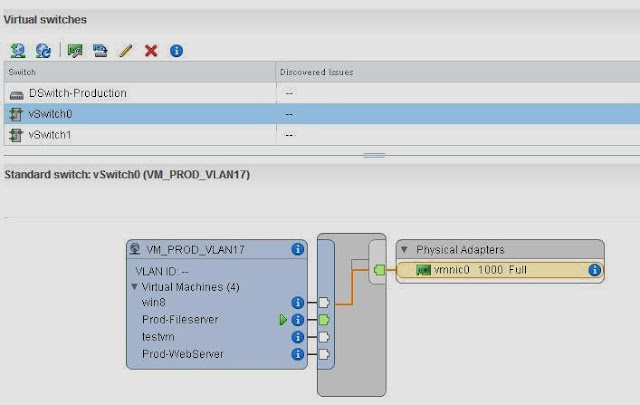
Now you can see the vmnic3 of the ESXi host (192.168.0.125) to the distributed switch DSwitch-Production.
I hope this is informative for you!!. Thanks for Reading. Be social and share it to social media if you feel worth sharing it.
Select your distributed switch from vSphere web client and click on Actions tab, Select Add and Manage Hosts.
Under Select a task to perform on this distributed switch wizard, Select Manage host networking and click on Next
Select your ESX/ESXi host from the list to perform the action. I have selected the host (192.168.0.125) and click on Next
Select Manage Physical adapters checkbox and click on Next.
Select the physical network adapter of the ESXi host to assign and click on Assign Uplink and click on Next. I have selected vmnic3 of ESXi host (192.168.0.125) to assign it to dvswitch
Select the uplink from the below list for vmnic3 adapter and click on Ok.
vmnic3 is assigned state for the Uplink2 for the dvswitch (DSwitch-Production) and click on Next.
Now you can see the vmnic3 of the ESXi host (192.168.0.125) to the distributed switch DSwitch-Production.
I hope this is informative for you!!. Thanks for Reading. Be social and share it to social media if you feel worth sharing it.
























































































![Robert Priest - People Like You and Me (2024) [Hi-Res]](http://www.dibpic.com/uploads/posts/2025-07/1751805912_lhttl01vuwv8a_600.jpg)





